Exploring NAD+ precursors: Why is supplementing with NMN the best option?
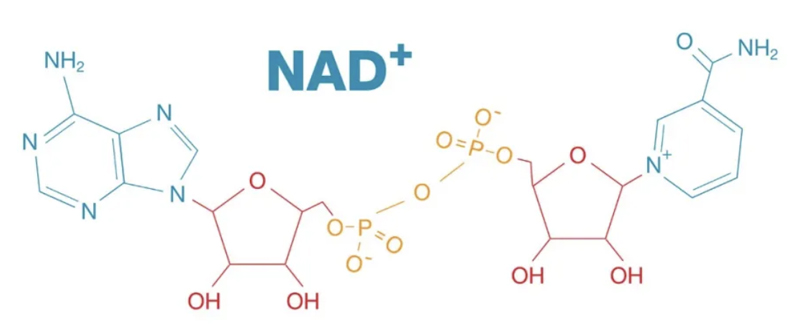
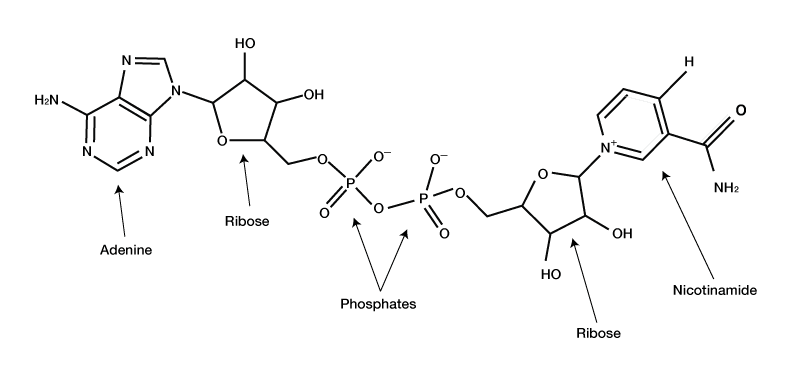
In recent years, NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), as an important coenzyme, has attracted much attention in the field of biochemistry and anti-aging.
NAD+ plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism, energy production, and DNA repair.
Direct supplementation of NAD+ is not an ideal option, but it is more effective to supplement its precursors such as NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide), NR (nicotinamide ribose) and NA (niacin).
What is NAD+?
We need to understand the concept of NAD+ and its scientific role. NAD+ is an essential coenzyme required for life and cellular function, present in all living cells and mainly involved in the energy metabolism process within cells.
NAD+ can repair damaged DNA, generate REDOX reactions, and help cells produce energy used by the body.
A number of studies have shown that NAD+ plays a key role in the process of energy metabolism,
DNA repair, and cell signaling, and is very effective in anti-aging and immunity enhancement.
As people age, the amount of NAD+ in the body also decreases year by year. After the loss of NAD+, the body will age significantly.
Studies have shown that the higher the level of NAD+ in the body, the more likely it is to improve health and slow the aging process. However, scientists do not recommend directly supplementing the body with NAD+.
Why can’t we supplement NAD+ directly?
In theory, directly supplementing NAD+ seems to increase the level of NAD+ in the body rapidly, which seems to be a good method.
But in reality, there are several key problems with this idea:
1. Molecular structure
NAD+ is a large molecule that is absorbed very inefficiently in the digestive tract.
The molecular structure of NAD+ is relatively complex, and it is not easy to enter the cell through the membrane.
2. Low bioavailability
Even when it enters the body by injection or consumption, the bioavailability of NAD+ remains low.
This means that directly supplemented NAD+ is difficult to use efficiently by cells, and thus cannot achieve the desired effect.
3. instability
NAD+ is relatively unstable and easily degraded both in vivo and in vitro, which also limits its effectiveness as a supplement.

For these reasons, scientists have turned to NAD+ precursors – substances that can be naturally converted into NAD+ in the body – in the hope of finding more effective ways to supplement.
Advantages of NAD+ precursors
NAD+ precursors provide an effective way to maintain and improve the level of NAD+ in vivo through their advantages of easy absorption and utilization and high bioavailability.
1. The molecule is small and easy to absorb
NAD+ precursors can more easily absorbed by the body and converted into NAD+.
They have a smaller molecular structure that allows them to more easily absorbed by the gut and directly into the cell through the cell membrane, thereby rapidly replenishing NAD+ levels in the body.
In contrast, NAD+ macromolecules are difficult to pass through cell membranes, and the oral absorption efficiency is extremely low.
2. High bioavailability and conversion efficiency
After the precursor substances enter the body, through a series of biochemical reactions, and finally efficiently converted into NAD+, its bioavailability is high.
Studies have shown that supplementation with NMN or NR (NAD+ precursor) significantly increases the level of NAD+ in vivo, which has been validated in many animal experiments and some human clinical trials.
Common NAD+ precursors
Many precursors of NAD+, such as NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide), NR (nicotinamide ribose) and NA (nicotinic acid), are very effective in anti-aging and immune enhancement.
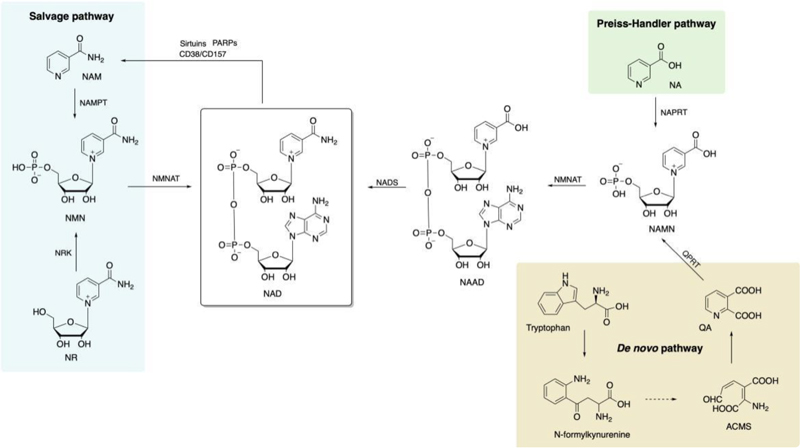
1. NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide)
NMN is one of the direct precursors of NAD+, and studies have shown that it can rapidly converted to NAD+.
Due to its superior bioavailability and significant health benefits, NMN is one of the most popular NAD+ precursors.
NMN has shown significant anti-aging effects in mice, improving metabolic function, increasing energy levels, and aiding DNA repair.
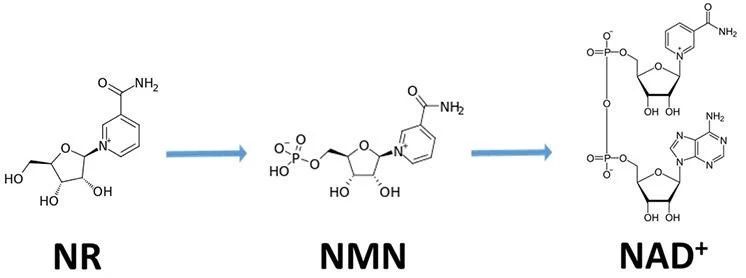
In humans, NMN is the most direct precursor of NAD+.
Taking NMN orally and converting it into NAD+ in the body to increase the ratio of NAD+ level is the most effective way to supplement.
2. NR (nicotinamide ribose)
NR is another potent NAD+ precursor, capable of conversion to NMN and further conversion to NAD+ via the NRK (nicotinamide ribokinase) pathway.
Multiple studies have shown that NR can enhance mitochondrial function, improve metabolic health, and have potential neuroprotective effects.
NR considered to highly effective and safe in increasing NAD+ levels in the body.
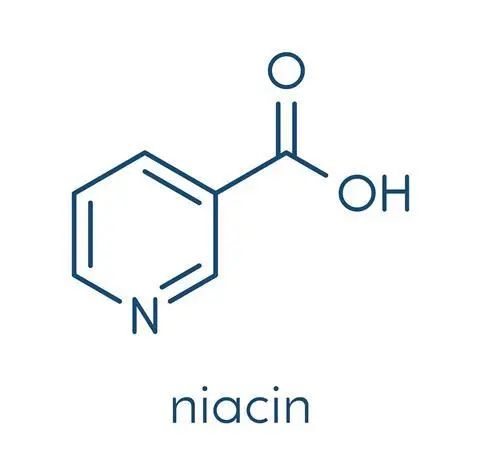
3. NA (Niacin)
NA is vitamin B3, which can also be converted to NAD+.
By regulating cholesterol levels, NA can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
NA widely recognized for its ability to improve cholesterol levels. It increases high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and lowers low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides.
Although NA can effectively raise NAD+ levels, its high dose intake may cause side effects such as skin flushing.
Nevertheless, NA remains a lower-cost, viable option, especially for those who are intolerant to other precursors.