792 genes reversed! Is NMN that powerful at relieving nerve damage?
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a common cause of death in trauma centers and one of the leading causes of adult death and disability worldwide. Globally, the annual incidence of TBI approximately 50 million, and China reports more than 700,000 TBI events each year, of which more than a quarter caused by severe TBI and adverse consequences account for more than half.
NMN provides new ideas for TBI

Although there are already methods such as surgical treatment, drug treatment and physical therapy, finding more effective and safer treatment methods has always been the goal of scientists. In recent years, some studies have discovered new methods, such as using NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) to increase NAD+ levels to protect neurons from excitotoxic damage. These studies provide new ideas and methods for treating TBI.
NMN reduces neurological damage after TBI
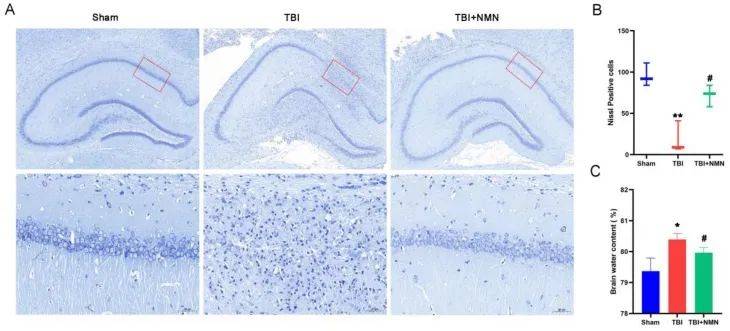
In order to explore the neuroprotective effect of NMN on TBI, the researchers tested the survival of nerve cells. They divided the rats into groups, namely sham operation group, TBI group and TBI+NMN group.
The results showed that the neuronal structure disappeared after TBI surgery, but compared with the TBI group, the TBI+NMN group had less loss of normal neuronal structure, indicating that NMN treatment reduced nerve damage in the hippocampal CA1 area after TBI. In quantitative statistics, the results showed that the number of nissl-positive cells in the sham operation group was 97±14 cells/field, while that in the TBI group was far less than that in the sham operation group (24±17 cells/field). Compared with the TBI group, the number of nissl-positive cells in the TBI+NMN group increased significantly, reaching 71±13 cells/field. In addition, measurements of brain water content also showed that NMN treatment also reduced brain edema.
NMN improves neurological function
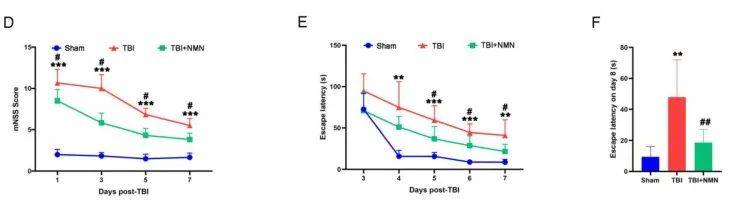
In order to observe whether NMN affects neurological function after TBI,
the researchers then conducted the mNSS score test and Morris water maze behavioral experiment. On days 1, 3, 5, and 7 after TBI,
the mNSS score in the TBI group was significantly higher than that in the sham operation group. However, after NMN treatment, the mNSS score was significantly reduced.
NMN reduces the number of reactive astrocytes and microglia
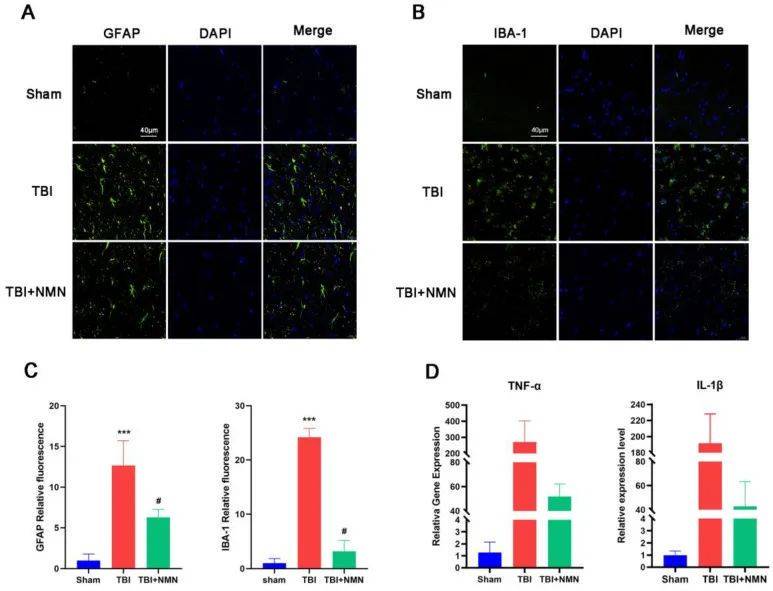
Previous studies have shown that neuroinflammation is one of the important mechanisms of secondary injury in TBI and is closely related to the activation of microglia and astrocytes. Therefore, the researchers further investigated whether NMN affects glial cell activation after TBI. Immunostaining of activated astrocyte-producing cells GFAP and microglia-producing cells Iba-1 showed that NMN treatment significantly reduced TBI-induced activated astrocytes and microglia in the CA1 area of the hippocampus,
which It was shown that NMN can help reduce the activation of these cells, thereby reducing the inflammatory response.
NMN reduces neuronal apoptosis after TBI
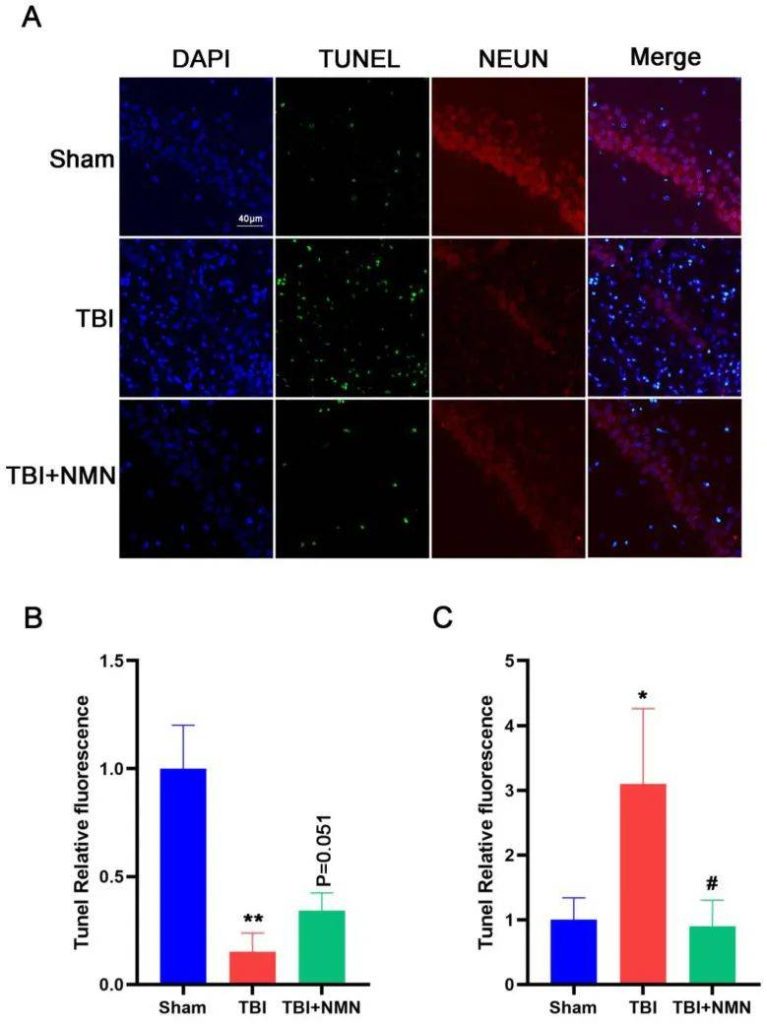
At the same time, researchers have found that improvements in neurological function after TBI are not only related to the reduction of inflammation,
but may also be directly related to neuronal damage.
Therefore, in order to evaluate neuronal apoptosis,
the researchers used the TUNEL method to take brain samples for double immunofluorescence staining to detect the expression of TUNEL and NEUN in the CA1 region.
The results showed that compared with the sham operation group,
the NEUN fluorescence intensity in the hippocampus decreased and the TUNEL fluorescence intensity increased after TBI,
which is consistent with the results of neuroinflammation. However, NMN significantly reduced the fluorescence intensity of TUNEL after TBI. Compared with the TBI group, the NEUN fluorescence intensity in the TBI+NMN group also increased significantly. These results indicate that NMN can reduce neuronal apoptosis.
NMN treatment reverses expression of genes after TBI
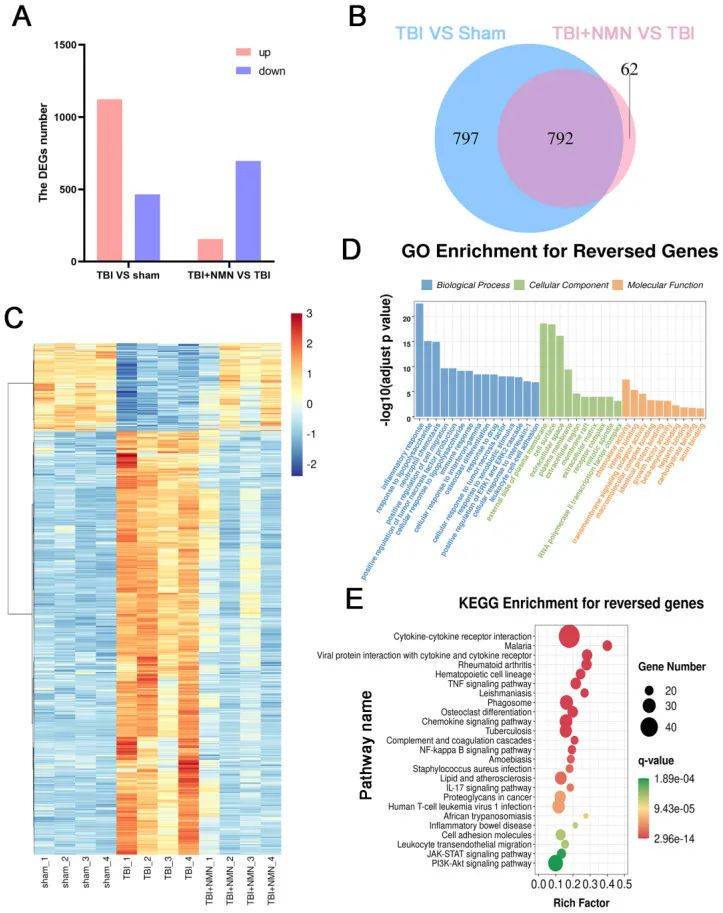
In order to further explore the relevant mechanisms of NMN's neuroprotective effect after TBI,
the researchers conducted transcriptome sequencing on the hippocampus of the Sham group, TBI group and TBI+NMN group.
The study found that NMN treatment could reverse 792 differentially expressed genes that appeared after TBI,
of which 656 genes were up-regulated and 136 genes were down-regulated.
In addition, these genes are related to inflammatory response, positive regulation of cell migration,
positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production, etc., and are enriched in multiple immune-related pathways. These results provide important clues for understanding the neuroprotective effects of NMN after TBI.
Taken together,
this study demonstrates that NMN treatment has a significant effect in alleviating neurological damage and improving neurological function caused by TBI. These findings provide important clues for understanding the neuroprotective effects of NMN after TBI and may provide a new strategy for the treatment of brain trauma. However, further research still needed to deeply understand the exact mechanism of action and clinical application of NMN.